







| Model | L400 | L600 | L800 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single plate area (m²) | 0.45 | 0.70 | 1.10 |
| Dimension A*B(mm) | 1835*489 | 2236*738 | 2446*838 |
| Corner hole diameter C(mm) | φ372 | φ585 | φ784 |
| Corner hole diameter D(mm) | φ150 | φ250 | φ300 |
| Corner hole diameter E(mm) | φ150 | φ250 | φ200 |
| Corner hole diameter F(mm) | φ100 | φ150 | φ200 |
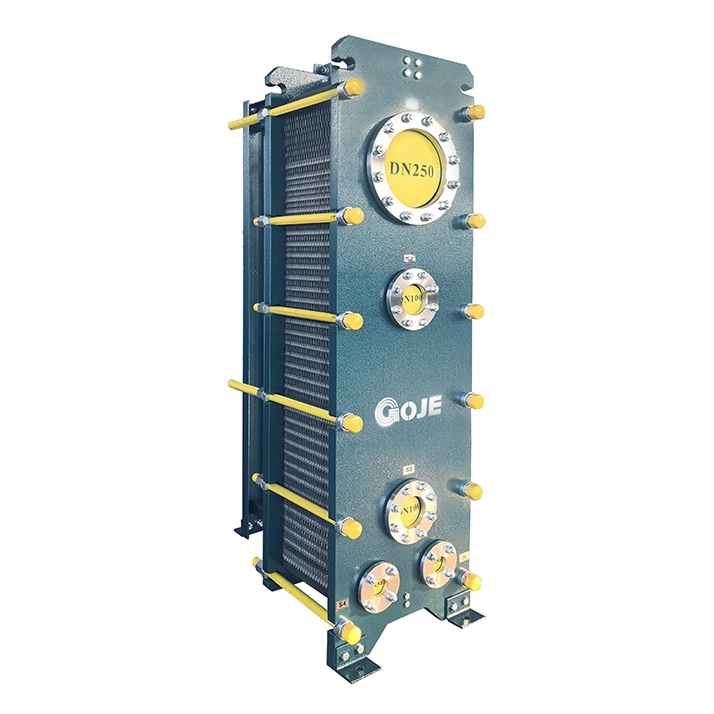
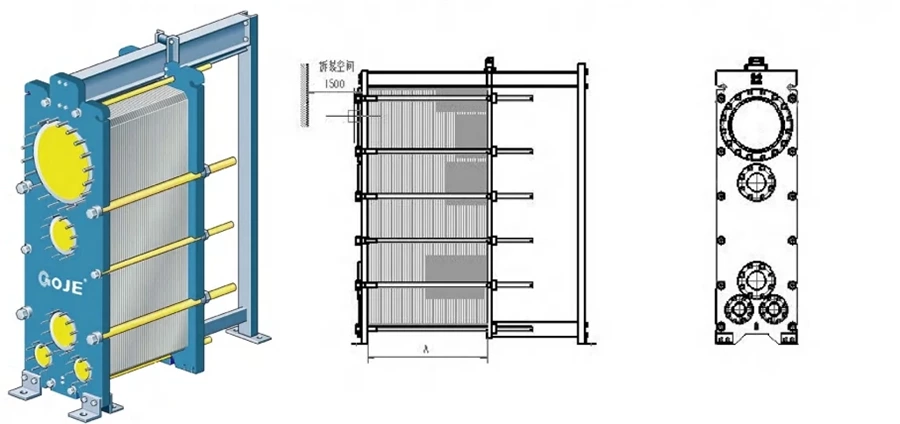

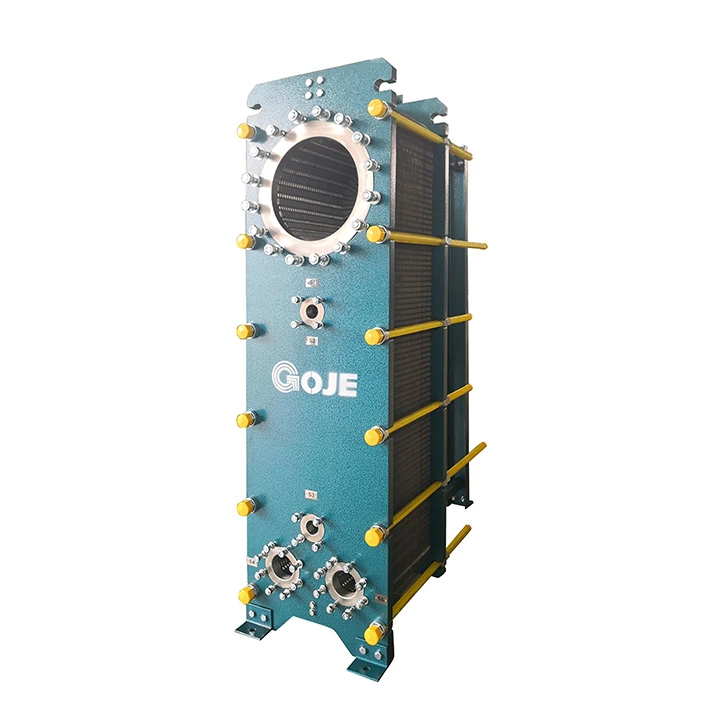
Plate condenser: It consists of two plates A and B, which can be divided into two types: semi-welded and detachable. A plate is a straight corrugated and B plate is transverse herringbone corrugated. A, B plates are arranged in the same arrangement, and the asymmetric channels is formed, and the ratio of wide and narrow channel is 1.88.
The condensing medium flows in a wide channel, and the cooling medium flows in a narrow channel, with small resistance drop. It can form a large plate condenser with high heat transfer efficiency, wide application range, compact structure, simple operation, convenient cleaning, disassembly and maintenance, and can meet the heating, cooling, condensation and waste heat recovery of the process. It is mainly used in chemical industry, petroleum, light industry, food, pharmaceutical industry, machinery, heating and heating industry, ship, metallurgy, mining, power industry, etc.
Plate condensers and plate heat exchangers are similar in structure and principle, both using metal plates stacked to form flow channels for heat exchange. However, depending on the application scenarios and functional requirements, there are the following key differences:

Plate condensers (specialized type) are specifically designed for the condensation process, which involves cooling gaseous media (such as refrigerants, steam) and converting them into liquid.
Plate heat exchangers (general-purpose) are used for heat exchange between liquids and liquids or between liquids and gases, with no phase change or only single-phase heat exchange.

Plate condensers may adopt asymmetric flow channels (such as a combination of wide and narrow channels) to optimize the distribution of gas-liquid two-phase flow and the discharge of condensate. And it needs to withstand higher pressure (especially on the refrigerant side), and the sealing requirements are stricter
Plate heat exchangers are usually symmetrical flow channels, emphasizing uniform fluid distribution and enhanced turbulence. It has a wide range of pressure adaptability. Just select the sealing material according to the medium.
The plate condenser processes media from gas to liquid (such as refrigerant R134a, ammonia vapor). The inlet is high-temperature gas (if the refrigerant can reach above 80℃), and the outlet is low-temperature liquid.
The medium processed by the plate heat exchanger is single-phase fluid (such as water-water, water-oil), and the temperature can be flexibly adjusted according to the application without the need for phase change.
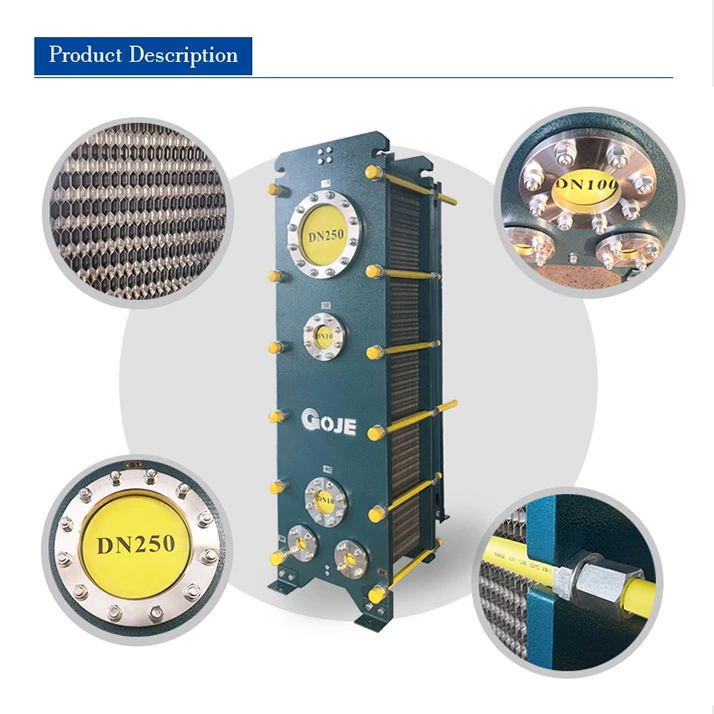

The material of the plate condenser should be corrosion-resistant (such as if the refrigerant may contain acidic impurities) and high-pressure resistant (such as titanium plates used in ammonia systems). During maintenance, attention should be paid to the residual condensate and scaling issues
Plate heat exchangers offer a wider range of material options (such as stainless steel and graphite), with a focus on medium compatibility.
| Plate Material Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Material | Application |
| SS304 | Drink water, None Corrosive Liquid, Oils, Fresh Steam etc. |
| SS316L | Well water, river water, closed circulating water and other water with complex components, Dilute sulfuric acid with temperature ≤ 50 ℃ and concentration ≤ 10% etc. |
| Titanium | Liquid that contains chlorine iron, Sea water etc. |
| Titanium Palladium Alloy | Higher temperature and corrosion resistance than titanium. |
| Nickel 20 | It is mainly used for caustic solution (NaOH, Koh, etc.) with high concentration (50% ~ 70%) and high temperature (boiling point). |
| Hastelloy C-276 | It has good corrosion resistance, almost not affected by Cl -, excellent corrosion resistance to various concentrations of sulfuric acid, and is one of the few materials that can be used in hot concentrated sulfuric acid, widely used in organic acids (such as formic acid, acetic acid), high temperature HF acid and a certain concentration of hydrochloric acid (< 40%), phosphoric acid (< 50%); chloride, fluoride. |
| Gasket Material Charactristics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Material | Working Temperature | Working Enviroment |
| NBR | -25~120℃ | Alkane, olefin and other non-polar media, all kinds of mineral oil, animal and vegetable oil, hot water, salt water, etc。 |
| EPDM | -50~170℃ | Superheated water, steam, atmospheric ozone, non petroleum based lubricating oil, weak acid, weak base, ketone alcohol, etc |
| HNBR | -25~150℃ | Crude oil, sulfur-containing oil and organic sulfur compounds, some heat transfer oil, new refrigerant 134a, etc |
| Viton | -25~150℃ | Nonpolar mineral oil, high temperature water vapor, sulfuric acid, chlorine water, phosphate with concentration above 98% |
Headquarters Address: No. 91, Shuanggao Road, Gaochun District, Nanjing,Jiangsu,China
Monday to Friday - 9:00 AM to 6:00 PM
Feel free to fill out our contact form below and our support team will get back to you within 24 hours.
We use cookies to collect information about how you use this site. We use this information to make the website work as well as possible and improve our services.more details